The Malay Archipelago is the archipelago between mainland Indochina and Australia. It has also been called the "Malay world," "Nusantara," East Indies, Indo-Australian Archipelago, Spices Archipelago and other names over time. The name was taken from the 19th-century European concept of a Malay race, later based on the distribution of Austronesian languages.
Situated between the Indian and Pacific Oceans, the archipelago of over 25,000 islands and islets is the largest archipelago by area and fourth by number of islands in the world. It includes Brunei, East Malaysia, East Timor, Indonesia, Papua New Guinea, and the Philippines. The term is largely synonymous with Maritime Southeast Asia.
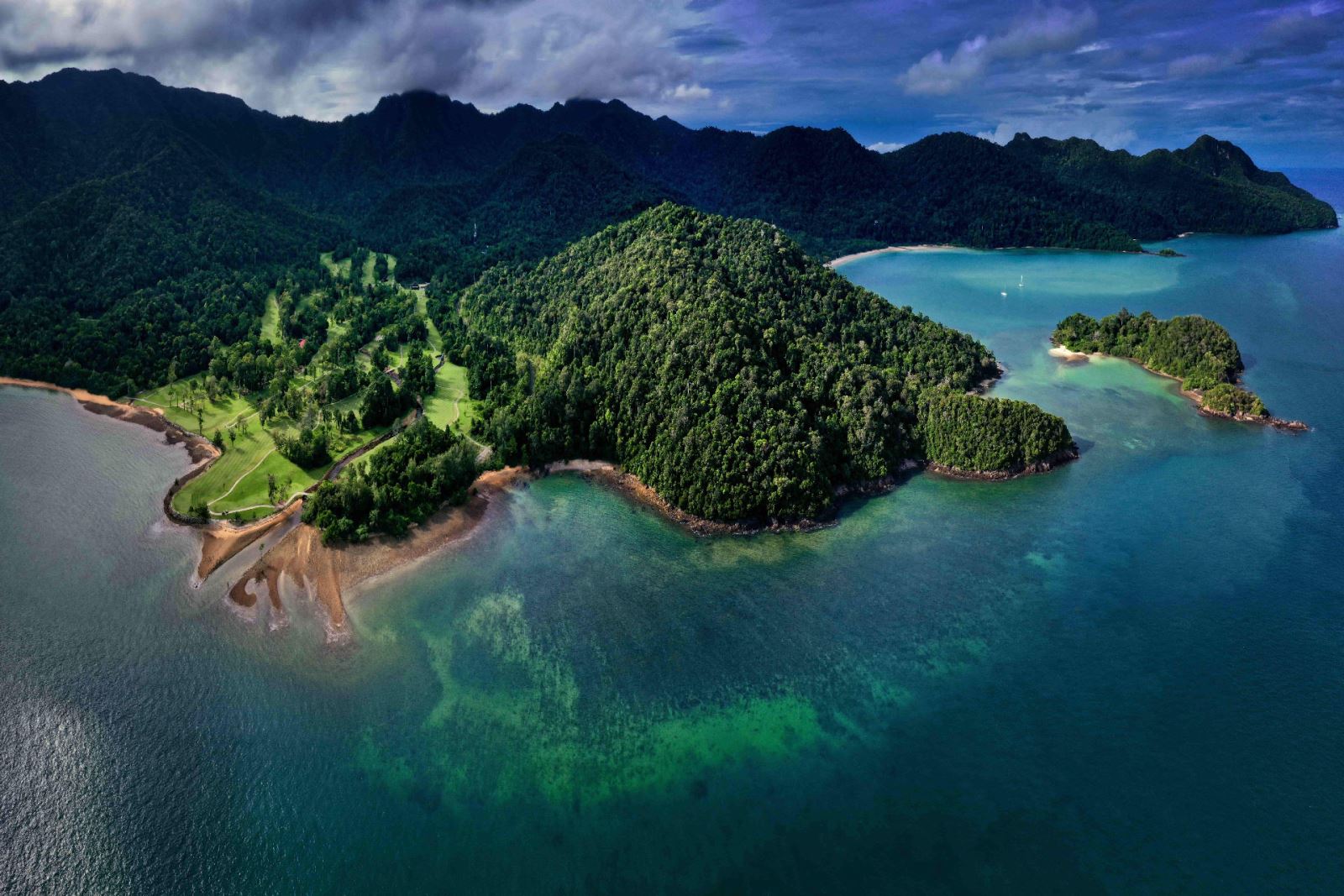

The land and sea area of the archipelago exceeds 2 million km2. The more than 25,000 islands of the archipelago comprise many smaller archipelagoes.
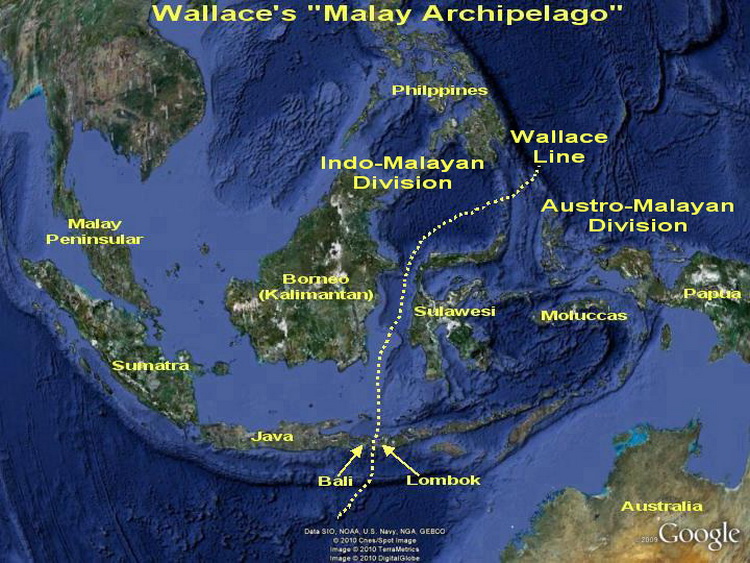
The major island groupings in the Indonesian Archipelago include the Maluku Islands, New Guinea, and the Sunda Islands. The Sunda Islands comrpise two island groups: the Greater Sunda Islands and the Lesser Sunda Islands.
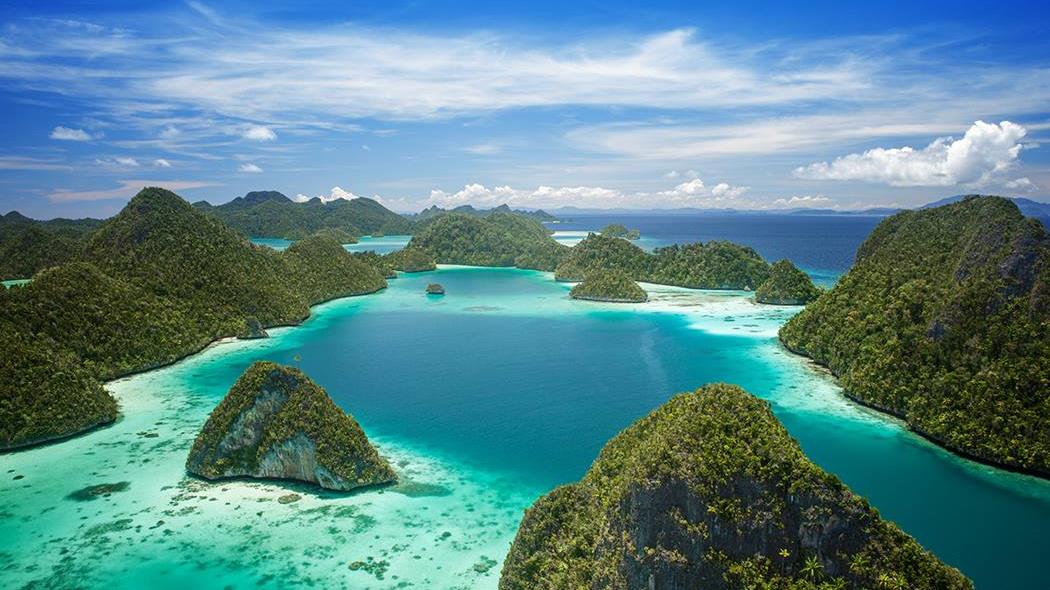

The major island groupings in the Philippine Archipelago include Luzon, Mindanao, and the Visayan Islands. The seven largest islands are New Guinea, Borneo, Sumatra, Sulawesi and Java in Indonesia; and Luzon and Mindanao in the Philippines.
Geologically, the archipelago is one of the most active volcanic regions in the world. Producing many volcanoes especially in Java, Sumatra and Lesser Sunda Islands region where most volcanoes over 3,000 m (9,843 ft) situated. Tectonic uplifts also produced large mountains, including the highest in Mount Kinabalu in Sabah, Malaysia, with a height of 4,095.2 m and Puncak Jaya on Papua, Indonesia at 4,884 m (16,024 ft). Other high mountains in the archipelago include Puncak Mandala, Indonesia at 4,760 m (15,617 ft) and Puncak Trikora, Indonesia, at 4,750 m (15,584 ft).
According to en.wikipedia











