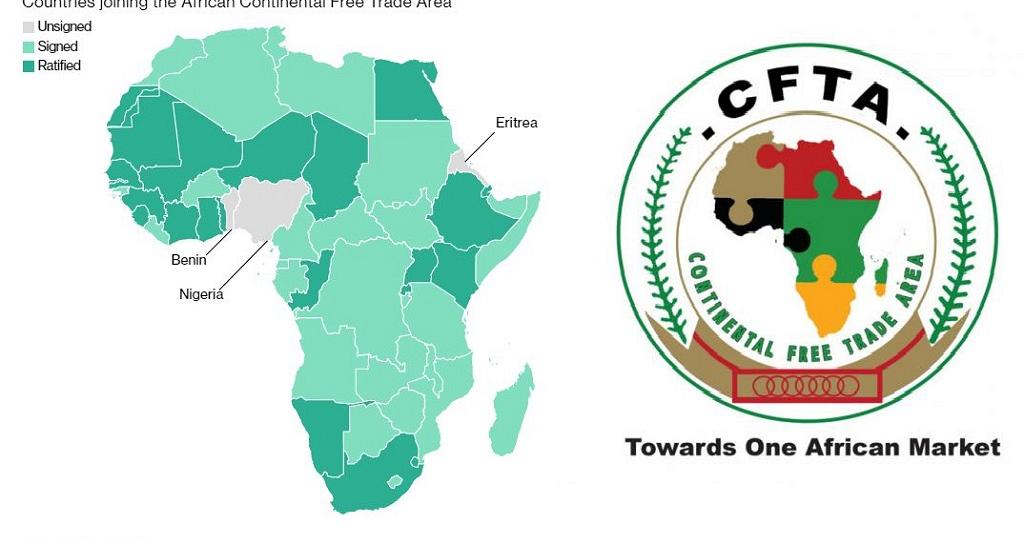
The African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) is a free trade area which as of 2018 includes 28 countries. It was created by the African Continental Free Trade Agreement among 54 of the 55 African Union nations. The free-trade area is the largest in the world in terms of the number of participating countries since the formation of the World Trade Organization.
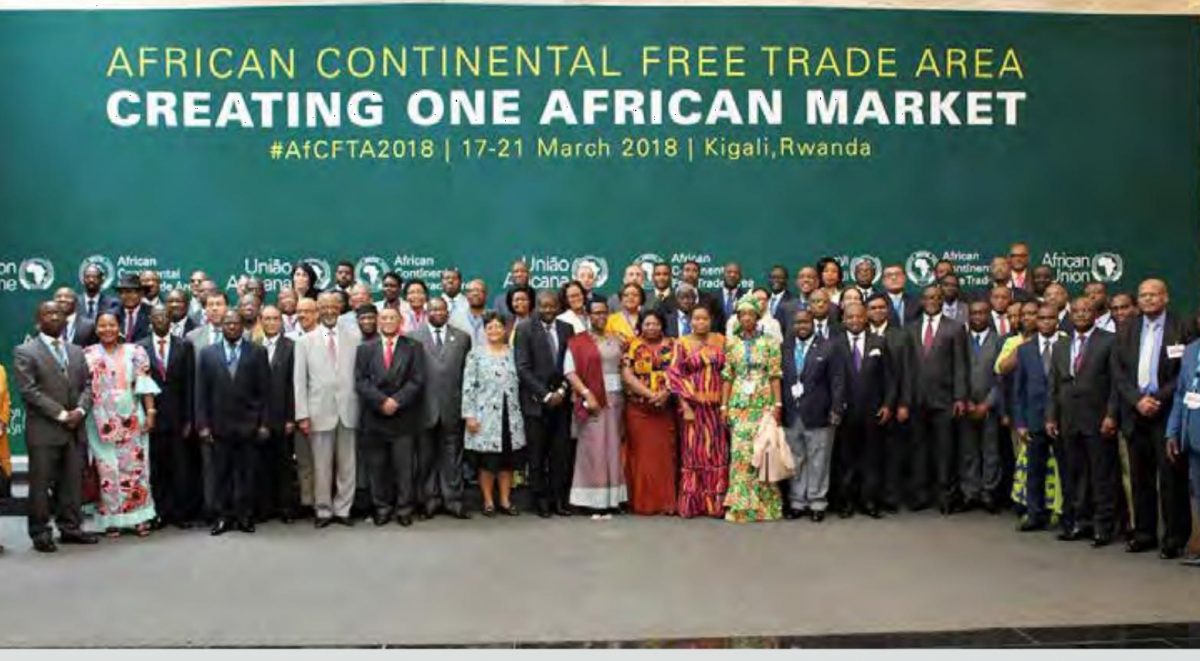

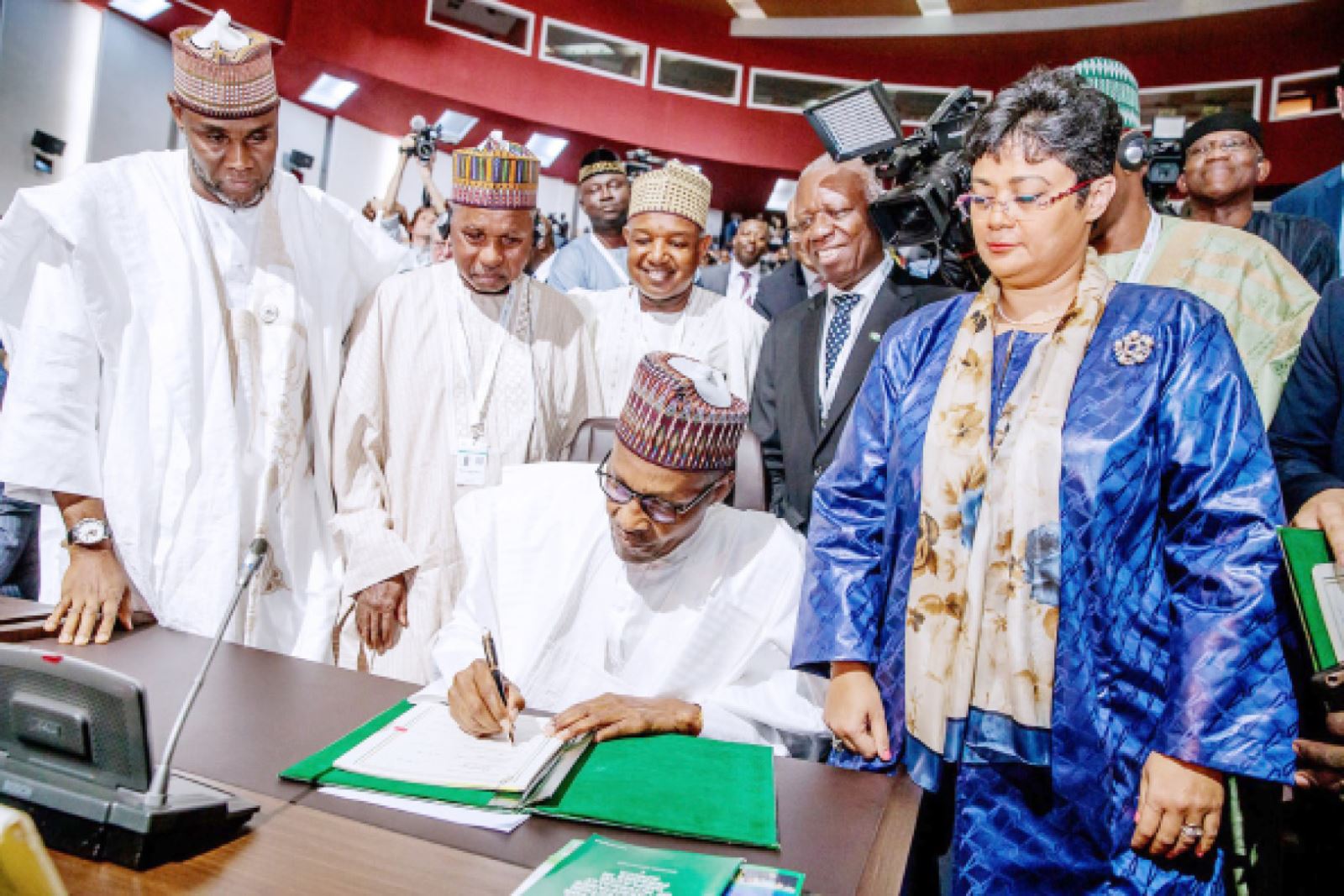
The agreement was brokered by the African Union (AU) and was signed on by 44 of its 55 member states in Kigali, Rwanda on March 21, 2018. The agreement initially requires members to remove tariffs from 90% of goods, allowing free access to commodities, goods, and services across the continent.

The United Nations Economic Commission for Africa estimates that the agreement will boost intra-African trade by 52 percent by 2022. The proposal was set to come into force 30 days after ratification by 22 of the signatory states.
The general objectives of the agreement are to:
• Create a single market, deepening the economic integration of the continent
• Establish a liberalised market through multiple rounds of negotiations

• Aid the movement of capital and people, facilitating investment
• Move towards the establishment of a future continental customs union
• Achieve sustainable and inclusive socio-economic development, gender equality and structural transformations within member states
• Enhance competitiveness of member states within Africa and in the global market

• Encourage industrial development through diversification and regional value chain development, agricultural development and food security
• Resolve challenges of multiple and overlapping memberships
According to en.wikipedia











